1 辽宁科技大学理学院, 辽宁 鞍山 114051
2 辽宁科技大学材料与冶金学院, 辽宁 鞍山 114051
激光熔覆是一种先进的表面改性技术, 具有对基体材料热影响区作用小、组织细密和基体的变形程度小等特点, 被广泛应用于再制造领域。稀土元素能够改善镍基合金涂层组织, 使熔覆层晶粒细小, 同时净化晶界。总结稀土氧化物在激光熔覆镍基合金涂层研究中的进展, 概述稀土氧化物的种类和性质, 结合稀土氧化物的作用机制研究其对镍基合金涂层的晶粒尺寸、稀释率、裂纹的影响, 分析涂层硬度、耐磨性、耐蚀性、抗氧化性等性能, 同时讨论其对涂层中硬质相的影响。最后对目前阶段稀土氧化物对激光熔覆镍基合金涂层研究中存在的问题和未来的发展方向进行了展望。
稀土氧化物 激光熔覆 镍基合金涂层 研究进展 rare earth oxide laser cladding nickel base alloy coating research progress

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Photonic Integrated Circuits Center, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Engineering Research Center of Optical Instrument and Systems, Ministry of Education, and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Modern Optical System, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
A kind of optical data storage medium based on electron-trapping materials, fluorescent ceramic, was developed by vacuum sintering technology. The medium shows sufficiently deep traps (1.67 and 0.77 eV). The properties of trap levels were researched by thermoluminescence curves, and the optical storage mechanism based on ion doping was proposed. More importantly, the data can be written-in by 254 nm UV light, and readout by heating (300°C). This work expands the application fields of fluorescent ceramics, and it is expected to promote the development of electron-trapping materials.
electron-trapping materials optical data storage Y3Al5O12 Ce3+ doping Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(4): 041602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Information Materials and Technology, South China Academy of Advanced Optoelectronics, South China Normal University, Higher-Education Mega-Center, Guangzhou 510006, China
2 National Center for International Research on Green Optoelectronics, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510006, China
3 State Key Laboratory for Modern Optical Instrumentation, College of Optical Science and Engineering, International Research Center for Advanced Photonics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
4 State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, School of Electronics and Information Technology, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510006, China
5 Jiaxing Key Laboratory of Photonic Sensing & Intelligent Imaging, Intelligent Optics & Photonics Research Center, Jiaxing Research Institute, Zhejiang University, Jiaxing 314000, China
Multi-lane integrated transmitter chips are key components in future compact optical modules to realize high-speed optical interconnects. Thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) photonics have emerged as a promising platform for achieving high-performance chip-scale optical systems. Combining a coarse wavelength-division multiplexing (CWDM) devices using fabrication-tolerant angled multimode interferometer structure and high-performance electro-optical modulators, we demonstrate monolithic on-chip four-channel CWDM transmitter on the TFLN platform for the first time. The four-channel CWDM transmitter enables high-speed transmissions of 100 Gb/s data rate per wavelength channel (i.e., an aggregated date rate of 400 Gb/s).Multi-lane integrated transmitter chips are key components in future compact optical modules to realize high-speed optical interconnects. Thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) photonics have emerged as a promising platform for achieving high-performance chip-scale optical systems. Combining a coarse wavelength-division multiplexing (CWDM) devices using fabrication-tolerant angled multimode interferometer structure and high-performance electro-optical modulators, we demonstrate monolithic on-chip four-channel CWDM transmitter on the TFLN platform for the first time. The four-channel CWDM transmitter enables high-speed transmissions of 100 Gb/s data rate per wavelength channel (i.e., an aggregated date rate of 400 Gb/s).
Journal of Semiconductors
2022, 43(11): 112301
强激光与粒子束
2022, 34(8): 081006
1 苏州大学电子信息学院,江苏 苏州 215006
2 香港理工大学电子及资讯工程学系,香港 999077
3 中山大学电子与信息工程学院,广东 广州 510275
针对跨海光通信系统,海岸两侧供电架构导致的能效问题是限制其容量的主要因素。多根单模光纤(M-SMF)复用是目前阶段提高通信海缆容量的主要解决方案。然而,海缆中可容纳的光纤数量往往受限于其机械特性和下缆难度,可容纳光纤数量目前通常限制在32以下。因此,高复用密度的空分复用技术有望在海缆通信领域中展现其优势。对基于多芯光纤(MCF)海缆的能效公式进行了理论推导,对比了MCF海缆与M-SMF海缆的能效特性,并分析多芯耦合器插损、芯间串扰等边际参数对系统总体能效的影响。结果证明:采用4芯光纤在跨大西洋海缆和跨太平洋海缆中的最优光纤数目分别为86和14;采用7芯光纤在跨大西洋海缆和跨太平洋海缆中的最优光纤数目分别为50和8。在海缆最大容纳光纤数目(32)情况下:4芯光纤在跨大西洋场景和跨太平洋场景中相比M-SMF海缆可以提升能效至2.50倍和1.13倍;7芯光纤在跨大西洋场景和跨太平洋场景中相比M-SMF海缆可以提升能效至3.20倍和1.13倍。
光通信 光纤特征 光纤表征 光复用 光学学报
2022, 42(15): 1506005
中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
为了同时满足激光装置对大口径反射镜面形精度和结构稳定性的控制要求,提出了一种反射镜多自由度解耦的多点夹持方式,通过限位实现对反射镜多自由度的控制,以此避免由夹持带来的附加面形。采用有限元法分析了所提方式的有效性,并通过实验验证了分析方法及该夹持方式的可行性,结果表明采用该反射镜夹持方式带来的附加面形较小,满足反射镜低应力附加夹持面形的要求。在此基础上,对45°倾斜放置的反射镜的面形进行了模拟,探究了不同夹持点位置分布对反射镜面形精度的影响规律,模拟结果表明:为了保证反射镜的面形精度,至少要有一个夹持点位于反射镜的长边。该研究成果对大口径反射镜夹持设计具有重要的指导意义。
光学设计 大口径反射镜 低应力夹持 面形精度 有限元模拟 中国激光
2020, 47(11): 1105004
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, School of Electronics and Information Technology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510006, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber and Cable Manufacture Technology, Yangtze Optical Fiber and Cable Joint Stock Limited Company, Wuhan 430073, China
3 Photonics Group, Merchant Venturers School of Engineering, University of Bristol, Bristol BS8 1UB, UK
4 e-mail: s.yu@bristol.ac.uk
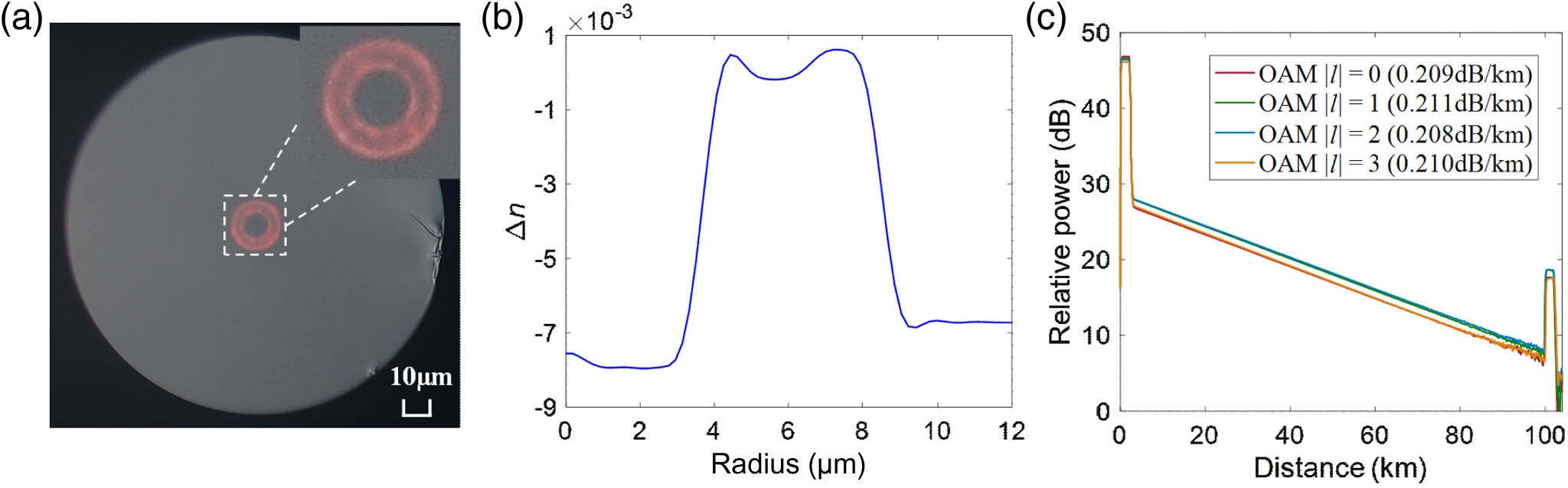
We experimentally demonstrate mode-division multiplexed (MDM) transmission using eight orbital angular momentum (OAM) modes over a single span of 100-km low-attenuation and low-crosstalk ring-core fiber (RCF). Each OAM mode channel carries 10 wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) signal channels in the C band, with each WDM channel in turn transmitting 16-GBaud quadrature phase-shift keying signal. An aggregate capacity of 2.56 Tbit/s and an overall spectral efficiency of 10.24 bit/(s · Hz) are realized. The capacity-distance product of 256 (Tbit/s) · km is the largest reported so far for OAM fiber communications systems to the best of our knowledge. Exploiting the low crosstalk between the OAM mode groups in the RCF, the scheme only requires the use of modular multiple-input multiple-output processing, and it can therefore be scaled up in the number of MDM channels without increasing the complexity of signal processing.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(7): 07001236
1 重庆大学 机械工程学院, 重庆 400030
2 中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
为实现大口径拼接光栅拼接误差的高频高精度补偿的工程应用, 提出了一种基于小口径反射镜补偿大口径拼接光栅压缩器拼接误差的方法。基于双程Z型压缩器, 分析了小口径反射镜补偿量与拼接误差的关系, 采用光线追迹法和夫琅禾费远场衍射原理定量计算了各拼接误差补偿后对远场能量分布的影响, 证明了该方法原理的正确性, 并得到了直接驱动光栅与反射镜补偿时的各误差容限, 结果表明该方法能极大降低拼接光栅的精度要求。
衍射光学 光学设计 光脉冲压缩 拼接光栅 超快光学 diffraction optics optical design optical pulse compression tiled-gratings ultrafast optics 红外与激光工程
2018, 47(11): 1142002
1 重庆大学机械工程学院, 重庆 400030
2 中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
分析随机并行梯度下降(SPGD)算法用于多路大型固体激光装置相干合成中校正动态相差的能力。首先介绍了SPGD算法实现相干合成的基本理论,利用数值模拟方法对算法进行了优化,实现了两路基于SPGD算法的波长为800 nm、带宽为30 fs光束的相干合成实验,验证了在外加10,15,20,25 Hz动态相差条件下算法的特性,并进一步模拟了动态活塞相差和指向性相差的校正过程,分析了不同相位噪声强度和频率对校正能力的影响,计算了控制带宽与光束路数、算法执行速度之间的关系。结果表明:远场强度分布的平方和是高能短脉冲激光相干合成的最佳性能评价函数;采用自适应增益的方式时,在保证算法稳定性的前提下,提高了算法的收敛速度;随着相位噪声强度和频率的提高,算法的有效控制带宽减小;算法执行速度越快,光束路数越少,则算法控制带宽越大;受限于器件性能,SPGD算法不适用于4路以上带宽为30 fs激光阵列的相干合成。
激光光学 相干合成 随机并行梯度下降算法 动态分析 控制带宽
1 重庆大学机械工程学院, 重庆 400030
2 中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
波前畸变会影响平行光栅对压缩器输出脉冲的可压缩性和远场焦斑的质量。结合光线追迹法和夫琅禾费远场衍射原理建立了平行光栅对压缩器理论模型。同时分析了输入脉冲的波前误差、光栅衍射面的形变以及光栅波像差对压缩器输出脉冲远场焦平面时空特性的影响, 并采用蒙特卡罗方法数值模拟分析了其误差容许范围。为高功率激光装置中平行光栅对压缩器中进行波前畸变和光栅质量的控制提供了理论参考。
非线性光学 波前畸变 光栅对压缩器 时空特性 光栅形变 波像差





